Deciphering Insulin Resistance
Understanding, Impact, and Management Strategies
In the intricate landscape of metabolic health, few concepts are as pivotal as insulin resistance. It’s a term that frequently surfaces in discussions surrounding diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Yet, its significance extends far beyond these conditions, affecting millions worldwide and significantly influencing overall health.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of insulin resistance, exploring its definition, underlying mechanisms, associated health risks, diagnostic methods, and effective management strategies.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition characterized by diminished responsiveness of cells to insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Under normal circumstances, insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is utilized for energy production. However, in individuals with insulin resistance, cells become less sensitive to insulin’s signals, impairing glucose uptake and leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
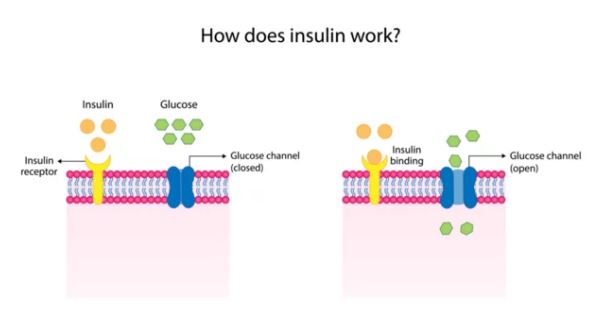
Understanding the Mechanisms
Several mechanisms contribute to the development of insulin resistance, including:
- Obesity: Excess adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, releases inflammatory cytokines and adipokines, which interfere with insulin signaling pathways.
- Lipid Accumulation: Intracellular lipid accumulation in tissues such as the liver and skeletal muscle disrupts insulin signaling and impairs glucose uptake.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation, triggered by factors such as diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity, contributes to insulin resistance by disrupting cellular signaling pathways.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic variations can predispose individuals to insulin resistance, although lifestyle factors play a significant role in its development.
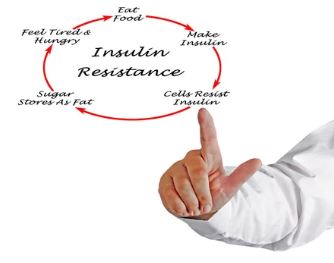
Health Risks Associated
Insulin resistance is not merely a metabolic inconvenience; it’s a precursor to a host of serious health conditions, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Prolonged resistance can overwhelm the pancreas’s insulin-producing capacity, leading to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Disease: It is intricately linked to the development of atherosclerosis, hypertension, and other cardiovascular risk factors.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): It contributes to the accumulation of fat in the liver, a hallmark of NAFLD, which can progress to more severe liver conditions.

Diagnostic Methods
Several diagnostic tests can assess insulin resistance and its associated metabolic abnormalities, including:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) and Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): These tests measure blood glucose levels after fasting or consuming a glucose solution, respectively.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): HbA1c reflects average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months and is used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes.
- Insulin Sensitivity Indices: These indices, derived from glucose and insulin measurements during oral glucose tolerance testing, provide insights into insulin sensitivity and resistance.
Management Strategies
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing this issue, several strategies have proven effective in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing associated health risks, including:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are foundational for managing insulin resistance.
- Natural Supplements: Certain dietary supplements, including omega-3 fatty acids, chromium, magnesium, and berberine, have shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
It is a complex metabolic condition with far-reaching implications for health and well-being. By understanding its mechanisms, associated health risks, diagnostic methods, and effective management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to address insulin resistance and reduce the risk of developing serious metabolic complications.
From lifestyle modifications to pharmacotherapy and natural supplements, a multifaceted approach is key to managing and promoting long-term metabolic health.
Integrative Medicine and Holistic Approaches
Dr. Keri Brown is a naturopathic physician with a passion for integrative medicine and holistic approaches to health. With extensive experience in treating insulin resistance and related metabolic disorders, Dr. Brown provides personalized care focused on addressing the root causes of illness and promoting long-term wellness.
Scheduling an Appointment
Insulin resistance is a complex metabolic condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. By embracing the principles of natural medicine and seeking guidance from experts like Dr. Keri Brown, individuals can address the underlying causes and promote lasting improvements in metabolic health.
Don’t hold you back – take charge of your health with a holistic approach that prioritizes natural remedies and personalized care.


