Understanding the Balance for Health
Navigating the Insulin Sensitivity vs. Insulin Resistance Spectrum
Insulin Sensitivity vs. Insulin Resistance. What is it? In the realm of health and wellness, the terms “insulin sensitivity” and “insulin resistance” frequently pop up, often accompanied by confusion and misconceptions. Yet, these concepts play crucial roles in our metabolic health, influencing everything from energy levels to weight management and disease risk.
In this blog, I’ll embark on a journey to demystify the delicate balance between insulin sensitivity and resistance, exploring what they mean, how they differ, and why they matter for our overall well-being.
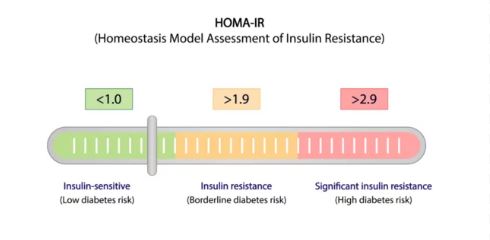
Insulin Sensitivity
The Body’s Metabolic Harmony
Let’s start with insulin sensitivity, often called the gold standard of metabolic health. When someone is insulin sensitive, their body does not efficiently respond to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas in response to glucose levels in the blood. Think of insulin as a key that unlocks cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy production. In insulin-sensitive individuals, cells respond to this signal, absorbing glucose from the bloodstream but ineffectively.
Issues of Insulin Sensitivity:
- Unstable Blood Sugar Levels: With inefficient glucose uptake by cells, blood sugar levels do not remain within a healthy range but do minimize spikes and crashes.
- Unenhanced Energy Levels: When cells can not efficiently utilize glucose, energy production is not optimized, leading to unsustained energy levels throughout the day.
- Weight Management Support: Insulin sensitivity is closely linked to the body’s ability to regulate fat storage and breakdown, potentially aiding in weight management efforts.
- Increase Disease Risk: Research suggests that insulin sensitivity may lead to insulin resistance and increase the risk of various health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Insulin Resistance
Disrupting the Metabolic Balance On the flip side, we have insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin’s signals, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This metabolic imbalance sets the stage for a cascade of negative effects, ultimately increasing the risk of developing various health problems.
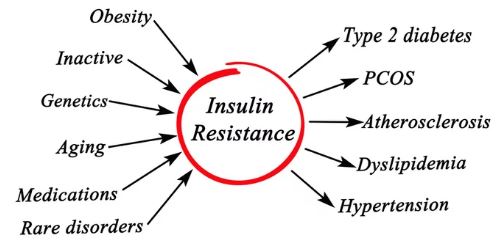
Factors Contributing to Insulin Resistance:
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to insulin resistance by reducing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Excess Weight: Obesity, particularly excess visceral fat around the abdomen, is strongly linked to insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats can promote insulin resistance over time.
- Genetics: While lifestyle factors play a significant role, genetics also influence an individual’s predisposition to insulin resistance.
Navigating the Balance with Insulin Sensitivity vs. Insulin Resistance
Strategies for Optimal Metabolic Health Achieving and maintaining a healthy balance between insulin sensitivity and resistance is key to promoting overall well-being. Fortunately, several lifestyle strategies can help support metabolic health:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to improve insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic function.
- Weight Management: Aim for a healthy weight through a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications tailored to individual needs.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance, so prioritize stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or hobbies that bring joy.
- Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night, as inadequate sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and negatively impact insulin sensitivity.
Insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance represent two ends of a spectrum that profoundly influences our metabolic health. By understanding the factors that influence these states and adopting lifestyle habits that promote insulin sensitivity, we can strive towards optimal well-being and reduce the risk of metabolic disorders.
Remember, small changes can make a big difference in achieving metabolic harmony and supporting long-term health.


